- Pascal's Chatbot Q&As
- Posts
- Perplexity: Trump and the Specter of Nazism: A Comparative Analysis of Rhetoric, Policy, and Public Perception. Gemini: Examining Connections Between Donald Trump and Nazism
Perplexity: Trump and the Specter of Nazism: A Comparative Analysis of Rhetoric, Policy, and Public Perception. Gemini: Examining Connections Between Donald Trump and Nazism
Perplexity: Tactics present serious concerns for democratic governance. Gemini: Comparison most potent when focused on tactics, rhetorical strategies & ideological underpinnings of associated figures.
Trump and the Specter of Nazism: A Comparative Analysis of Rhetoric, Policy, and Public Perception
by Perplexity, Deep Research. Warning, LLMs may hallucinate!
The comparative analysis of Donald Trump's political career and the historical record of Adolf Hitler's regime remains one of the most controversial topics in contemporary political discourse. While some dismiss such comparisons as hyperbolic, a growing body of historical analysis examines distinct parallels in rhetorical strategies, policy approaches, and governance philosophies. This report examines documented connections between Trump's political persona and Nazi-era precedents, extending to key figures in his administration and support network.
Historical Patterns and Rhetorical Parallels
The relationship between Trump's political rhetoric and Nazi-era communication strategies has been examined by numerous scholars and political observers. Trump's rhetoric contains several elements that invite comparison to Hitler's oratorical approach, particularly in their emotional appeals and characterizations of perceived enemies.
Rhetorical Similarities and Public Messaging
Both Trump and Hitler demonstrated remarkable skill in using inflammatory language to cultivate fervent support. Trump's denunciation of opponents consistently highlighted claims that "he alone" could fix America's problems, which bears striking similarity to Hitler's insistence on the "Fuehrerprinzip" (leader principle) that advocated for vesting all power in a single leader1. This cultivation of a savior narrative proved effective in mobilizing supporters who felt disenfranchised.
The persistent use of dehumanizing language represents another concerning parallel. Trump has repeatedly warned that immigrants are "poisoning the blood" of the United States, echoing language used by Hitler in "Mein Kampf"2. Such rhetoric serves to create clear distinctions between in-groups and out-groups, a hallmark of fascist communication.
Both figures also displayed what analysts have called a "readiness to lie" and exceptional talent in projecting declarations with minimal regard for factual accuracy1. This approach to truth became a powerful tool in reshaping public discourse. Trump's emphasis on rally sizes and audience responses similarly recalls Hitler's mass events, which served as visible demonstrations of popular support1.
Media Exploitation and Control of Narrative
Hitler and his Propaganda Minister Joseph Goebbels expertly exploited mass media of their time-radio, film, and print. Similarly, Trump has leveraged both traditional and social media platforms to amplify his message1. While Hitler suppressed independent media, Trump has instead worked to delegitimize mainstream media through persistent accusations of "fake news," creating parallel information ecosystems that reinforce existing beliefs.
A key difference lies in their approach to media control: Hitler eliminated competing voices, while Trump operated in an environment where independent media persisted. However, the "stovepiping" of information in America-where citizens' choice of news sources reinforces polarization-has weakened the effectiveness of competing narratives1.
The Second Trump Administration: Controversial Appointments and Actions
The second Trump administration has seen several appointments and policy initiatives that have further fueled comparisons to authoritarian regimes of the 1930s and 1940s.
Elon Musk's Controversial Role and Statements
Elon Musk, appointed to co-head the Department of Government Efficiency in Trump's second term, has been a lightning rod for Nazi comparisons. During Trump's second inauguration celebration at the Capital One Arena, Musk made a gesture interpreted by many observers as resembling a Nazi salute7. While Musk claimed he was saying "my heart goes out to you," his actions were celebrated by neo-Nazi and white nationalist figures, including Thomas Sewell (who described it as a "Donald Trump White Power moment") and Nick Fuentes (founder of the white nationalist Groypers group)7.
Musk has further courted controversy through his engagement with Germany's far-right Alternative for Germany (AfD) party. In a video address to the AfD, Musk stated that Germany needed to "move beyond" the "guilt" of the past, adding that "children should not be guilty of the sins of their parents, let alone their great grandparents"8. He urged Germans to "take pride in Germany and being German" and warned against "multiculturalism that dilutes everything"8. These comments mirrored the AfD's position that Germany should stop atoning for Nazi crimes-a statement that Dani Dayan, chairman of the World Holocaust Remembrance Center, condemned as "an insult to the victims of Nazism"8.
Stephen Miller's White Nationalist Connections
Stephen Miller, a senior policy adviser to Trump, has promoted white nationalist literature and pushed racist immigration stories, according to leaked emails reviewed by the Southern Poverty Law Center9. Miller recommended the novel "The Camp of the Saints," a text distributed by white nationalist Social Contract Press that depicts a dystopian future where non-white refugees invade France9.
In his communications, Miller showed particular interest in immigration policies from the 1920s that were based on eugenics. The Immigration Act of 1924, which Miller has referenced approvingly, severely limited immigration from certain parts of the world and was praised by Hitler in "Mein Kampf"9. Yale Law School professor James Q. Whitman noted that "Hitler talks about the law in 'Mein Kampf'" and "suggests that the U.S. was the only country making the type of progress the Nazis were trying to establish"9.
Institutional Transformation and Use of State Power
Perhaps the most concerning parallels involve the transformation of government institutions and the use of state power against perceived enemies or undesirable groups.
ICE Operations and Comparisons to Secret Police
Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) under Trump has been described by some experts on authoritarian regimes as increasingly resembling a secret police force10. ICE operations have expanded to include what critics characterize as arbitrary arrests, indefinite detentions, and family separations.
In recent cases that have alarmed civil liberties organizations, ICE officers reportedly deported three children who are U.S. citizens along with their Honduran-born mothers, as well as separating a Cuban-born mother from her 1-year-old daughter11. The American Civil Liberties Union and National Immigration Project described these actions as "shocking-although increasingly common-abuse of power"11. Reports indicate that these deportations occurred with virtually no opportunity for the individuals to speak with lawyers or family members11.
Such operations have led some scholars to draw parallels to historical secret police forces. In Nazi Germany, the Gestapo used informants who "penetrated all levels of society, producing an atmosphere of distrust"10. While ICE operates within a constitutional framework with theoretical checks on its power, critics argue that its increasingly aggressive tactics and targeting of vulnerable populations bear concerning similarities to authoritarian enforcement mechanisms.
Strategic Initiatives: Project 2025 and Project Esther
Project 2025, developed by the conservative Heritage Foundation, represents what some see as a blueprint for consolidating executive power. Based on a controversial interpretation of the unitary executive theory, the project envisions the entire executive branch under complete presidential control12. Critics have characterized it as an "authoritarian, Christian nationalist plan that would steer the U.S. toward autocracy"12.
A related initiative, Project Esther, aims to cast pro-Palestinian protesters as Hamas supporters and utilize anti-terror and immigration laws to suppress campus demonstrations13. According to reporting, the Trump administration's strategy reflects elements of this plan, with moves to pull university funding over antisemitism allegations and arrest protesters13. Critics argue this represents an effort to expand executive power under the guise of fighting antisemitism while primarily targeting political opposition.
Comparative Analysis: Key Differences and Contextual Factors
While the parallels between Trump's approach and Nazi-era tactics merit serious examination, important differences exist that must be acknowledged for a complete analysis.
Biographical and Historical Context
Trump rose to power as a celebrity businessman who took over an existing political party, while Hitler built his own nationalist movement from minor factions1. Trump was raised in privilege with inherited wealth, while Hitler experienced severe hardship before his political rise1. The United States in the 21st century also maintains democratic institutions with greater resilience than the fragile Weimar Republic.
Trump's attempt to disrupt the peaceful transfer of power, while deeply concerning, did not lead to the complete collapse of democratic governance. The U.S. has also maintained independent judiciary and media sectors, though both have faced significant pressure1.
Academic and Expert Assessments
General Mark Milley, who chaired the Joint Chiefs of Staff during Trump's first presidency, reportedly told author Bob Woodward: "No one has ever been as dangerous to this country as Donald Trump... Now I realize he's a total fascist. He is the most dangerous person to this country"1. Such assessments from those who worked closely with Trump lend weight to concerns about his authoritarian tendencies.
Scholars who specialize in fascism and authoritarianism have increasingly noted the relevance of historical comparisons. Historian Peter Hayes has stated that certain comparisons between current political developments and the pre-World War II era are "increasingly relevant"15. However, most careful analyses conclude that while Trump exhibits concerning authoritarian tendencies, the comparison to Hitler is "intrinsically controversial and necessarily tentative. The differences are manifold, but so are the similarities"1.
Conclusion: Implications for Democratic Institutions
The parallels between Trump's political style and Nazi-era tactics present serious concerns for democratic governance. The exploitation of grievance politics, dehumanization of marginalized groups, attacks on institutional checks and balances, and cultivation of personality cults all represent strategies employed by historical authoritarian movements.
A reasoned assessment suggests that Trump is not Hitler-their personal backgrounds, historical contexts, and many aspects of their governance differ substantially. Yet the rhetorical and strategic similarities warrant continued vigilance. As one analysis concluded: "Trump is no Hitler-unless the American people enable him to be one"1.
The enduring lesson from this comparative analysis is that democratic backsliding rarely happens overnight. Instead, it occurs through the gradual erosion of norms, institutional independence, and public trust. By understanding these historical patterns, citizens and institutions can better recognize and respond to threats to democratic governance before they become insurmountable.
The study of these parallels is not merely academic-it provides essential context for understanding contemporary political dynamics and the resilience of democratic institutions in the face of authoritarian pressures.
Examining Connections Between Donald Trump and Nazism: A Comparative Analysis
by Gemini Advanced, Deep Research with 2.5 Pro. Warning, LLMs may hallucinate!
A. The Gravity of Historical Analogy
The act of drawing parallels between contemporary political figures or movements and historical Nazism is an endeavor laden with profound historical weight and significant potential for misapplication.1 Nazism, with its systematic atrocities and the unparalleled horror of the Holocaust, has become a potent metaphor for absolute evil in modern consciousness.2 Consequently, any such comparison demands exquisite care, meticulous precision, and a deep understanding of the distinct historical contexts involved. This report approaches the subject with the requisite caution, aiming to provide a dispassionate and analytical examination of alleged connections and distinctions based on the available evidence. The objective is not to assert a direct equivalence, which many scholars and commentators find problematic, but rather to scrutinize the basis, nature, and validity of the comparisons that have been made in academic and public discourse concerning Donald Trump, his political movement, and Nazism.
The very frequency with which such analogies are invoked in contemporary discussions, particularly in relation to Donald Trump and associated political phenomena 2 , may itself be indicative of underlying societal anxieties. Often, these comparisons emerge during periods of heightened political polarization and when democratic norms and institutions are perceived to be under threat.4 In this sense, the deployment of the Nazi analogy can become a political act, intended to sound an alarm or to frame current events by referencing a widely understood historical nadir of Western civilization. This suggests that the analysis must extend beyond the mere content of the comparisons to consider the context in which they arise and the motivations or concerns that fuel them.
Furthermore, the vigorous debate surrounding the appropriateness of applying the Nazi analogy to Trump or Trumpism reveals fundamental disagreements in the interpretation of both historical Nazism and contemporary political developments.1 Scholars and commentators often focus on different facets—some highlighting rhetorical similarities, others emphasizing divergent institutional powers or the absence of state-sponsored genocide. This divergence underscores that there is no universally accepted set of criteria for what constitutes a "valid" or "accurate" comparison. The process of historical analogy is inherently interpretive, and the selection of comparative elements can be influenced by the analyst's framework and focus. Therefore, this report will strive to present the spectrum of viewpoints found within the provided materials, acknowledging the contested nature of these comparisons.
B. Report Aims and Methodology
This report aims to conduct a critical analysis of the connections, parallels, and divergences between aspects of Nazism and characteristics associated with Donald Trump, his political rhetoric, policies, leadership style, and affiliated figures or initiatives. The analysis will be grounded exclusively in the provided research materials. The methodology involves a comparative approach, juxtaposing core tenets and practices of Nazism with documented statements, actions, policies, and scholarly interpretations related to Donald Trump. It will meticulously examine areas such as ideological frameworks, rhetorical strategies, policy proposals and implementations, and the nature of leadership, drawing connections and distinctions as supported by the textual evidence. The report will navigate the complexities of this sensitive topic by adhering to an evidence-based framework, focusing on specific points of comparison raised within the academic and journalistic sources at hand.
II. Understanding Nazism: Core Ideological and Operational Pillars
To undertake a comparative analysis, a clear understanding of the subject of comparison—Nazism—is essential. Nazism, the totalitarian movement led by Adolf Hitler in Germany, was characterized by a distinct set of ideological tenets and operational methods that resulted in catastrophic consequences.
A. Foundational Ideology
The ideology of Nazism was a virulent amalgamation of several core beliefs. Intense nationalism formed its bedrock, promoting the idea of a superior German "Aryan race" and advocating for the unification of all German-speaking peoples.9 This nationalism was inherently exclusionary and aggressive, rejecting international cooperation and envisioning German dominance. Fundamental to Nazi ideology was a profound and eliminatory antisemitism, which portrayed Jewish people as an existential threat to the German nation and ultimately led to the Holocaust.9 Nazism staunchly rejected the principles of liberalism, democracy, the rule of law, and universal human rights, viewing them as decadent and weakening.9 Instead, it emphasized the complete subordination of the individual to the state and demanded unwavering obedience to its leaders.9 The concept of the "Volksgemeinschaft" (people's community) was central, though it was a community defined by racial purity and ideological conformity, with "undesirables" systematically excluded and persecuted.
An important characteristic of Nazi ideology was its "anti-intellectual and atheoretical" nature, which placed paramount importance on the will of the charismatic dictator, Adolf Hitler, as the "sole source of inspiration of a people and a nation".10 This ideological fluidity, paradoxically, allowed the regime to be ruthlessly pragmatic in its pursuit of power while maintaining its core tenets of racial hatred and nationalism. The absence of a rigid, systematically developed theoretical framework, coupled with the Führerprinzip (leader principle), meant that Nazi ideology was highly personalized. Hitler's pronouncements could become de facto policy, allowing for tactical shifts and adaptations as long as they served the overarching goals of the regime. This implies that when comparing Nazism to other movements, it is crucial to look for similar patterns of personalized leadership that may override established doctrines or legal norms, rather than seeking a perfectly mirrored, static ideology.
B. The Führerprinzip and Totalitarian Control
The Führerprinzip was a cornerstone of Nazi governance, institutionalizing Hitler's absolute authority.9 All power flowed downwards from the Führer, demanding strict and unquestioning obedience at every level of the state and party apparatus. This principle effectively dismantled any remnants of democratic accountability or collective decision-making. The Nazi Party, under Hitler's supreme command, established a totalitarian state that permeated every aspect of German life.9 This control was maintained through a sophisticated and brutal machinery of repression, including the ubiquitous secret police (Gestapo), the SS (Schutzstaffel), a vast network of concentration and extermination camps, and the systematic suppression of all forms of political dissent and social nonconformity.10
C. Propaganda and Mass Manipulation
Adolf Hitler demonstrated a keen, albeit cynical, understanding of mass psychology and the effective use of propaganda.10 He articulated the view that propaganda should target the "capacity of the least intelligent" and that its truthfulness was far less important than its ultimate success in swaying public opinion.10 The Nazi regime deployed a relentless and multifaceted propaganda machine that utilized all available cultural and informational media—press, radio, film, arts, and education—to indoctrinate the populace and cultivate support for its policies.10 Elaborately staged mass rallies, such as those held in Nürnberg, were designed to create an overwhelming spectacle of power and unity, fostering a sense of collective identity and awe for the regime.10 Nazi insignia, uniforms, and public rituals further reinforced this image of omnipotence. This pervasive propaganda was complemented by an apparatus of terror, ensuring that fear and coercion played a significant role in maintaining control.10
D. Racial Hygiene and Eugenic Policies
A defining and horrific aspect of Nazism was its commitment to "racial hygiene" and eugenics. These pseudoscientific theories provided the ideological justification for policies aimed at creating a "pure" Aryan master race.9 Nazi eugenics led to programs of compulsory sterilization for individuals deemed "hereditarily unfit".12 The most notorious of these initiatives was the "Euthanasia Program," codenamed Aktion T4, which systematically murdered tens of thousands of institutionalized patients with mental and physical disabilities.9 These individuals were deemed "life unworthy of life" (LebensunwertesLeben) and a "financial burden" on the state, and their elimination was framed as a necessary step to "cleanse" the Aryan race and restore its supposed racial integrity.11
Significantly, the Nazi eugenics program initially targeted disabled individuals withinthe German "Aryan" population itself.12 An estimated 250,000 such individuals, the vast majority of them German "Aryans," fell victim to these clandestine killing operations.12 This internal "cleansing" demonstrates that the Nazi concept of "racial purity" was an inwardly focused project of exclusion even before it fully manifested as the externally focused genocide of the Holocaust. This phased approach to defining and eliminating "undesirables" reveals a progressive narrowing of who belonged to the "master race," starting with those deemed biologically or socially unfit even within their own defined ethnic group. This historical progression suggests that when analyzing other ideologies or policies for potential eugenic echoes, it is important to look not only for overt racism against out-groups but also for rhetoric or policies that devalue, marginalize, or seek to eliminate specific segments within a proclaimed in-group based on perceived fitness, worthiness, or conformity. These early eugenic programs also served as a testing ground, both methodologically and ideologically, for the later mass murder of Jews and other targeted groups.
III. Donald Trump and the Political Landscape: Key Characteristics and Ideological Underpinnings
Understanding the political phenomenon associated with Donald Trump requires an examination of his political profile, key ideological stances, and the figures and movements connected to his ascent and governance.
A. Political Profile and Ideological Stances
Donald Trump's political career has been characterized by notable shifts in party affiliation, having been registered as a Republican, a member of the Reform Party, and a Democrat at various points before ultimately securing the presidency as a Republican.13 His political rhetoric is widely recognized for its populist, nationalist, and confrontational style.14 This approach often emphasizes themes of national crisis, societal division, and the paramount importance of loyalty to his person and movement.14 He has been a prominent promoter of conspiracy theories, such as the "birtherism" claim that questioned the legitimacy of Barack Obama's presidency.13 His communication strategy frequently employs direct, unfiltered language, emotional appeals resonating with voter insecurity, and promises of restoring a perceived past national "greatness".14
B. Key Figures and Associated Movements
Several individuals and movements have become closely associated with Donald Trump's political trajectory and policy agenda, and feature prominently in comparisons to historical or ideological precedents.
Stephen Miller, a senior policy adviser during Trump's first term, is described as having promoted white nationalist literature and racist immigration narratives.15 His ideology is seen as a key influence on Trump's anti-immigrant policies, including the controversial family separation policy at the border.15 Miller's rhetoric has included statements such as "America is for Americans and Americans only!" and he has publicly advocated for mass deportations, including the establishment of "large scale staging grounds for removal flight".16
Elon Musk, the prominent entrepreneur, has also entered the political sphere in ways that have drawn comparisons. He has publicly supported the Alternative for Germany (AfD) party 17 , a German political party characterized by xenophobic and anti-immigrant stances.19 During a rally celebrating Trump's second inauguration, Musk made a gesture that was widely interpreted by observers, particularly in Germany where such gestures are illegal, as a Nazi or fascist Roman salute.20 Furthermore, Musk has been accused of engaging in discourse that downplays the historical guilt associated with the Holocaust.19
The Alternative for Germany (AfD) party itself has been a subject of significant controversy. German authorities have officially labeled the AfD as a "right-wing extremist" organization, concluding that it aims to exclude certain population groups from equal societal participation and subject them to unconstitutional, unequal treatment, thereby assigning them a legally devalued status.19 The party is noted for its xenophobic, anti-immigrant, and anti-Muslim positions, and an ethnic-based understanding of German identity deemed incompatible with Germany's constitution.19 Figures associated with Trump's political circle, such as then-U.S. Vice President JD Vance and Senator Marco Rubio, have offered support or defense for the AfD, criticizing German efforts to classify it as extremist.19
Project 2025 is a comprehensive policy agenda developed by conservative organizations, notably the Heritage Foundation, in anticipation of a potential second Trump administration. It has been described as targeting immigrants and transgender individuals, attacking abortion access, proposing measures to erode voting rights, censoring curricula, and prohibiting protest and free speech.24 Some critical analyses connect the ideological underpinnings of Project 2025 to historical currents of Nazi-inspired eugenics and scientific racism, particularly through organizations like the Pioneer Fund.25 The Pioneer Fund, established in the 1930s with ties to Nazi eugenicists, actively promoted ideas of racial hierarchy, positioning white people at the apex and Black people at the bottom.25
Closely related is Project Esther, another Heritage Foundation document. While ostensibly framed as a "National Strategy to Combat Antisemitism," it has been heavily critiqued by groups like Jewish Voice for Peace as a deceptive strategy primarily aimed at dismantling the Palestine solidarity movement in the United States.24 Critics argue that Project Esther deploys false claims of antisemitism and terrorism against activists and organizations supportive of Palestinian rights, serving as a smokescreen for a broader racist, anti-Palestinian, and Christian Nationalist agenda.24
The pattern of international networking and mutual endorsement observed between figures associated with Trumpism (such as JD Vance, Marco Rubio, and Elon Musk) and far-right European parties like Germany's AfD 17 points towards the emergence of a transnational populist and nationalist movement. This is not merely a collection of isolated national phenomena; rather, there appears to be a conscious alignment and a shared worldview among these disparate groups. This shared ideology often revolves around common touchstones such as staunch anti-immigration stances, anti-establishment sentiment, and a definition of national sovereignty rooted in exclusionary terms. Trump himself has often expressed admiration for authoritarian leaders and nationalist movements globally, further reinforcing this perception of a connected international front. Understanding these transnational linkages is vital for analyzing the resilience, adaptability, and broader appeal of these political ideologies, suggesting that the "Trump phenomenon" should be viewed within this larger global context.
The alleged strategy underlying "Project Esther" 24 —whereby the legitimate and serious issue of antisemitism is purportedly weaponized to suppress criticism of Israeli policies and simultaneously advance a Christian Nationalist agenda—exemplifies a broader political tactic. This tactic involves co-opting genuine concerns or historical traumas to shield controversial political objectives or to attack opponents. This creates a complex and often disingenuous dynamic where authentic issues become entangled with, and potentially subverted by, political maneuvering. Such "smokescreening" or "decoy" arguments aim to make opposition to the underlying, less popular agenda appear as insensitivity or hostility towards the "smokescreen" issue itself (e.g., framing opposition to Project Esther's broader goals as tolerance of antisemitism). This significantly complicates public discourse, making it exceedingly difficult to address the genuine issue (in this case, antisemitism) separately from the political agenda it is allegedly being used to advance. Vigilance against such instrumentalization of sensitive issues is therefore crucial in political analysis, particularly when accusations as grave as Nazism or antisemitism are involved, given the immense emotional and historical weight these terms carry.
IV. Comparative Analysis: Examining Potential Connections and Divergences
The core of this inquiry lies in a comparative examination of Nazism and various aspects associated with Donald Trump and his political movement. This section will dissect ideological frameworks, rhetorical strategies, policy proposals, and leadership styles to identify areas of alleged similarity and clear distinction, based on the provided source materials.
A. Ideological Frameworks: Nationalism, Racial Narratives, and Anti-Democratic Sentiments
Ideology forms the conceptual backbone of any political movement, shaping its goals, its definition of allies and enemies, and its relationship with existing societal structures.
1. Nationalism and "Us vs. Them"
Nazi ideology was characterized by an extreme and aggressive form of nationalism, encapsulated in slogans like "Deutschland über alles" (Germany Above All) 30 , which emphasized German racial superiority and a destiny of dominance, rejecting international cooperation in favor of national self-interest defined in expansionist and racial terms.9
Comparatively, Donald Trump's political platform has been prominently marked by the "America First" slogan 30 , a strong articulation of populist nationalism.14 This nationalist stance has been echoed by associated figures like Stephen Miller, who reportedly proclaimed, "America is for Americans and Americans only!".16 Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov, in a critical assessment, explicitly drew a parallel between Trump's "America First" concept and the Nazi-era slogan "Germany Above All".30
While both ideologies clearly exhibit potent nationalist currents that create a sharp distinction between an "in-group" (the nation) and various "out-groups," the foundational basis and the primary targets of exclusion differ significantly when considering their respective historical contexts and ultimate aims. Nazi nationalism was intrinsically and explicitly tied to a biologically determinist racial theory that culminated in systematic persecution and genocide.9 Trump's nationalism, as depicted in the sources, while frequently exclusionary and often targeting specific groups such as immigrants 14 , operates within a vastly different legal and societal framework. Its exclusionary basis appears to be more frequently articulated along lines of culture, national origin, or perceived economic threat, rather than an explicitly genocidal ideology as was central to Nazism. Thus, while the rhetorical function of nationalism—unifying an "us" against a "them"—may present superficial parallels, the substantive content, ideological underpinnings, and historical outcomes of that nationalism are markedly distinct. The Nazi variant was a core driver of state-sponsored mass murder, aggressive warfare, and territorial conquest. Trump's nationalism, as portrayed in the materials, has focused more on issues such as border control, economic protectionism, and the reassertion of a particular vision of American identity and sovereignty. Therefore, direct slogan comparisons like "America First" versus "Germany Above All" can be misleading if not deeply contextualized with the distinct ideological content and the vastly different historical consequences associated with each. The impact and intent of the nationalism serve as crucial differentiators.
2. Racial and Minority Narratives
A defining feature of Nazism was its virulent antisemitism, which was not merely a peripheral prejudice but a fundamental ideological pillar that led directly to the Holocaust.9 The Nazi regime was built upon a belief in Aryan racial superiority and was committed to the purging of "undesirables," with Jewish people being the primary target, defined by "race" rather than religious affiliation.9 This ideology manifested in comprehensive eugenics policies, including the T4 Euthanasia Program for the disabled and compulsory sterilization laws, all aimed at achieving supposed racial purity.9 The Nuremberg Laws institutionalized this racial ideology by stripping Jews of citizenship and prohibiting intermarriage.12
In the context of Donald Trump and his associated movements, certain rhetoric and policy proposals have drawn comparisons to these Nazi racial narratives. Trump has used language such as immigrants "poisoning the blood of our country" 8 , a phrase that directly echoes Adolf Hitler's statements in Mein Kampf.8 He has also reportedly referred to undocumented immigrants as "animals" and asserted that "they're not humans".8 Stephen Miller, a key policy advisor, is documented as having promoted white nationalist literature and focusing on crimes allegedly committed by nonwhite individuals.15
Furthermore, critiques of Project 2025, a policy blueprint for a potential second Trump term, allege ideological roots in Nazi-inspired eugenics, particularly through connections to the Pioneer Fund.25 The Pioneer Fund, with historical links to Nazi eugenicists, advocated for theories of racial hierarchy that positioned white people as superior, particularly to Black people.25 Trump's promotion of the "birtherism" conspiracy theory against Barack Obama 13 and policies aimed at dismantling Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) initiatives 26 are also cited in this context.
The alleged connection between Trump-era policy thinking, particularly as embodied in Project 2025, and organizations like the Pioneer Fund 25 is particularly noteworthy. The Pioneer Fund's historical ties to Nazi eugenicists and its role in distributing Nazi propaganda in the United States 25 suggest a potential, disturbing through-line of "scientific racism." This ideology, though adapting its presentation over decades, appears to retain core hierarchical and exclusionary ideas. If these documented links are accurate, it implies that certain contemporary policy proposals might not be novel inventions but rather a resurgence or repackaging of discredited eugenic and racial hierarchy theories. These theories, while having historical connections to Nazism, are adapted to a new socio-political context, for instance, by shifting primary focus from Jewish people (as in Nazism) to other groups such as Black people, migrants, and Muslims, as noted in some analyses.25 This underscores a need to meticulously scrutinize the intellectual and historical provenance of contemporary policy ideas, especially those concerning race, immigration, and social hierarchy, to ascertain if they are drawing from ideologies with dangerous historical precedents. The reported "rebranding" of scientific racism as "human biodiversity" 26 is identified as a key tactic in this contemporary adaptation.
3. Attitudes Towards Democratic Institutions and Rule of Law
Nazism fundamentally rejected democratic principles, the rule of law, and human rights, instead emphasizing the subordination of all societal elements to the state and demanding absolute obedience to its leaders.9 The Nazi regime systematically dismantled democratic institutions, a process significantly accelerated by the Enabling Act of 1933, which effectively granted Hitler dictatorial powers.35
Concerning Donald Trump and Trumpism, various statements and actions have raised concerns about attitudes towards democratic norms and institutions. Rhetoric often frames political opponents not merely as adversaries with differing views but as existential dangers to the nation.14 The events surrounding the January 6th attack on the U.S. Capitol, and Trump's role in challenging the 2020 election results, are central to these concerns.33 Comparisons of Trump administration actions, particularly in defying court orders related to deportations, to an "American Gestapo" have been made by critics.32 Trump's use of terms like "vermin" to describe political opponents 8 has also drawn historical parallels. Ironically, Trump himself has likened the Biden administration to a "Gestapo administration" when alleging political persecution.32 His public attacks on the judiciary 4 and the proposals within Project Esther to criminalize certain forms of protest and target faculty members for their views 24 further contribute to this picture. Academic analysis suggests that while Trump sought to reshape national identity through means such as education policy, he encountered significant institutional resistance within the U.S. democratic framework, a contrast to Hitler's ability to achieve total control.35 Nevertheless, some scholars identify "fascist elements" within Trump's movement and point to clear anti-democratic tendencies.4
A recurring pattern evident in the materials related to Trump is the systematic delegitimization of opposing voices and institutions. This includes the press (frequently labeled "fake news" or "enemy of the people" 39 ), the judiciary when rulings are unfavorable 38 , political opponents (characterized as "vermin" or disloyal 8 ), and specific population groups. While this campaign of delegitimization is not identical to the Nazi regime's complete and violent dismantling of all opposition, it can serve to erode public trust in essential democratic checks and balances. Such erosion may, over time, create a political environment more amenable to authoritarian measures. The sustained effort to discredit and neutralize opposition, as suggested by the rhetoric and certain actions, shares a functional similarity with broader authoritarian tactics aimed at creating an environment where the leader's narrative and exercise of power face minimal challenge. Even if this does not culminate in a full-scale dictatorship akin to Nazi Germany, the long-term effects can include a significant weakening of democratic culture, an increase in political polarization, and a greater public willingness to accept restrictions on rights or due process, particularly when applied to groups designated as "enemies" or "others."
Table IV.A: Comparative Overview of Core Ideological Tenets
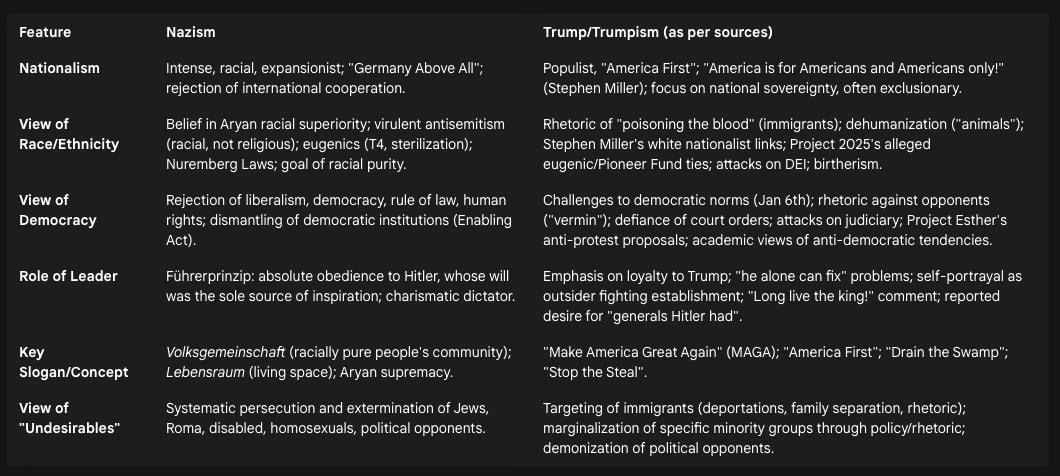
B. Rhetoric, Propaganda, and Media Engagement
The methods by which political movements communicate their messages, mobilize support, and interact with information ecosystems are critical areas for comparison.
Continue reading here (due to post length constraints): https://p4sc4l.substack.com/p/perplexity-trump-and-the-specter
